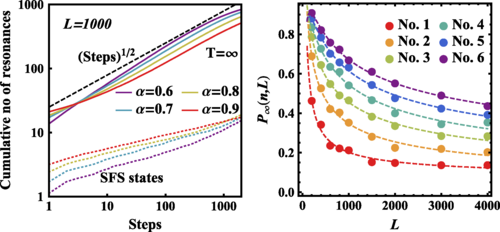
Just published in Physical Review Letters, our latest work on a quantum spin glass with unusual dynamics. Spin glasses and many-body localization (MBL) are prime examples of ergodicity breaking, yet their physical origin is quite different: the former phase arises due to rugged classical energy landscape, while the latter is a quantum-interference effect. Here, we study quantum dynamics of an isolated 1D spin glass under application of a transverse field. At high energy densities, the system is ergodic, relaxing via a resonance avalanche mechanism, that is also responsible for the destruction of MBL in nonglassy systems with power-law interactions. At low energy densities, the interaction-induced fields obtain a power-law soft gap, making the resonance avalanche mechanism inefficient. This leads to the persistence of the spin-glass order, as demonstrated by resonance analysis and by numerical studies. A small fraction of resonant spins forms a thermalizing system with long-range entanglement, making this regime distinct from the conventional MBL. The model considered can be realized in systems of trapped ions, opening the door to investigating slow quantum dynamics induced by glassiness.
Rademaker and Abanin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 260405 (2020)