Title: Determinant quantum Monte Carlo study of exciton condensation in the bilayer Hubbard model
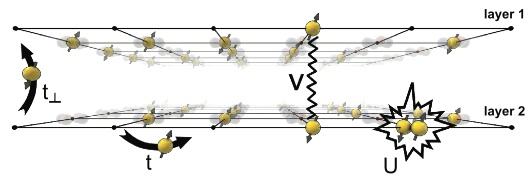
Abstract: We studied the possibility of exciton condensation in a strongly correlated bilayer extended Hubbard model using determinant quantum Monte Carlo. To model both the on-site repulsion U and the interlayer interaction V we introduced an update scheme extending the standard Sherman-Morrison update. We observe that the sign problem increases dramatically with the inclusion of the interlayer interaction V, which prohibits at this stage an unequivocal conclusion regarding the presence of exciton condensation. However, enhancement of the interlayer tunneling results suggest that the strongest exciton condensation tendency lies around 10–20% p/n doping. Magnetic properties and conductivity turn out to be relatively independent of the interlayer interaction.
Reference: Louk Rademaker, Steve Johnston, Jan Zaanen, and Jeroen van den Brink, Phys. Rev. B 88, 235115 (2013)
Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics